Do I have a hearing loss?
Over 10 million people in the UK have some form of hearing loss, this equates to 1 in 6 of the population.
Hearing is measured in a scale referred to as decibels (dB). The dB scale is used to determine whether a hearing loss present in comparison to normal hearing.
If a hearing loss is present then the dB scale will indicate how severe that loss is. This information is then used to determine whether intervention is required or not.
During your hearing assessment an examination will be carried out and the results will be displayed as an audiogram. An audiogram is a graphical display of the hearing test results and an explanation will be provided by your Audiologist.
Hearing is tested at various frequencies since all sounds constitute a variation of frequencies.

Categories of hearing loss
The scale below indicates the different levels of hearing loss (HL).
Normal hearing
(<20dB HL)
Mild
(20-40dB HL)
You have trouble hearing or understanding soft speech and whispers, or speech over background noise.
Moderate
(41-55 dB HL)
You have trouble hearing or understanding regular speech up close or regular speech in a quiet office environment, background noise may be an even greater challenge when trying to hold a conversation.
Moderately severe
(56-70 dB HL)
You have trouble hearing or understanding everyday conversations or a telephone ringing. Many situations become difficult, TV level may be quite high, regularly asking people to repeat themselves.
Severe
(71-95 dB HL)
You can only hear loud sounds such as very loud speech, sirens or a door slamming. Most situations will be difficult especially talking on the telephone, and even a one to one conversation may be a challenge.
Profound
(95+ dB HL)
This category is the most challenging when trying to participate in regular conversations in almost all situations. Sounds around the home may not be heard, clanging of cutlery, door bells, phone rings are all an example of sounds that may go undetected.
Audiogram
As described earlier your hearing test results will be plotted on an audiogram as shown below. An audiogram is a visual representation of your hearing.
This is a typical audiogram for a person with normal hearing:

And this is a typical audiogram for a person with age-related hearing loss:
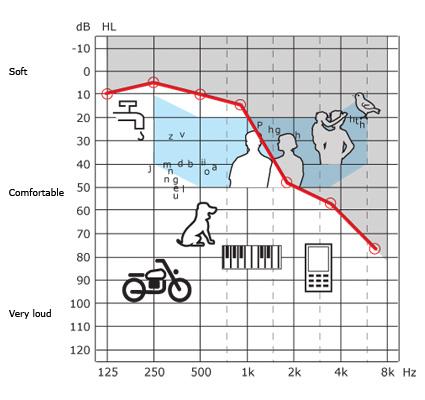
The results obtained from the hearing test will provide a strong indication of whether a hearing instrument (or two) will be beneficial.
Signs and symptoms of hearing loss
The degree of hearing loss may vary from one person to another, some more mild whereas others may have more of a severer loss.
Hearing loss can be gradual or even sudden, it can be bilateral (both ears) or unilateral (one ear).
If you think you or someone else may have hearing difficulties and have suspected this for a while then you are not alone.
On average it can take 10 years for people to address their hearing loss.
In order to get an accurate diagnosis it is important to have your hearing assessed by a hearing care professional. If you or someone you know would answer yes to a few of the below then this may indicate that a further assessment is required.
Social:
- Frequent repetition required when conversing
- Struggle to follow a conversation with 2 or more participants
- Some people sound like they are mumbling
- Struggle to hear in the presence of background noise such as restaurants, meeting rooms, conferences, lectures, gatherings.
- Finding that the TV needs to be turned up to be able to hear
- Being told you speak loudly
- Difficulty hearing children or women
- Rely on facial expressions or lip read to help follow the conversation
Emotional:
- Avoid environments where you need to be able to hear well
- Are embarrassed by not being able to hear in certain situations
- Feel fear or anxiety when meeting new people
- Feel isolated or withdrawn from your surroundings
- Regularly feel tired from effort of listening
Medical:
- Have a family history of hearing loss
- Experience a ringing or buzzing sound from time to time or all the time (may be a sign of tinnitus)
- Taking medications that may impact your hearing (ototoxic drugs)
- Suffer from vertigo or balance problems